Osteocartilage degeneration is a degenerative disease in which the deformed form of the intervertebral disc, the form of height reduction and stratification. The pathology is diverse, but can be combined into several syndromes. Several stages of osteochondrosis are distinguished according to the severity of the symptoms, changes in the disc surrounding its structure. Before treating osteochondrosis in the cervical area, it is important to find out why various medications, physical therapy and surgical methods are needed.
General information
Osteochondrosis in the cervical spine is most common in people over the age of 35, but its manifestations are sometimes observed between the ages of 18 and 30. The cervical vertebra consists of vertebrae, the most flowing one is usually affected by the fifth, sixth and seventh.
The intervertebral discs between vertebrae are the special shape of the most durable cartilage bone connection. They provide the spine’s ability to withstand significant loads and its mobility.
Each disc contains:
- The core of the flesh (jacket) is gel-like mass.
- A dense fiber ring around the disc core.
- Two thin white fiber cartilage plates covering the disks above and below.
The intervertebral disc uses ligaments to connect to the body of the vertebrae.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Among those over the age of 20, the ships feeding the discs are overgrown. In the future, these structures receive all the necessary substances by diffusion from many arranged vertebrae, but these processes are usually not sufficient to allow normal metabolism in the disc.
Osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebra is most commonly formed under the following causes:
- Genetic tendency.
- Anatomical abnormalities in the cervical area.
- overweight.
- A sedentary lifestyle is related to a sedentary work and lacks physical fatigue.
- Trauma to the spine of the neck, including bruises, cracks.
- Metabolic diseases in the body.
- age-related changes.
- Excessive physical effort.
- Frequent psychological and emotional stress.
These factors aggravate the nutrition of the intervertebral disc. Therefore, the pulp pulpos are flattened and they become less elastic. The load on the fiber annular rings increases, accompanied by their stretching, where cracks form.
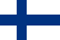
In the context of this degenerative change, the disc can protrude toward the spine. Stimulation of longitudinal ligaments rich in nerve ends is accompanied by local pain.

As the disease progresses, the posterior longitudinal ligament rupture occurs and the intervertebral disc herniation into the cerebrospinal pelvis is called hernia. Meanwhile, rooster syndrome caused by recent cerebrospinal spinal stimulation of local autoimmune inflammation is developing. If the radiated spinal artery is squeezed, it will interfere with the blood supply to the spinal cord.
Osteocartilage degeneration of the cervical vertebra is accompanied by the formation of osteoflexus - the product of bone tissue in the body, the process of vertebrae. These formations can also squeeze the spinal nerves or the roots of the spinal cord.
The first sign
Osteochondrotalosis in the initial stage of cervical thoracic cavity is accompanied by tension, and rapid fatigue of muscles in this area. Then, discomfort, pain on the neck, neck, shoulders, shoulders, worsen during tilting, and the head turns.
Dizziness, headache - Another sign of cervical osteochondrosis in men, males. Sometimes, a person will feel pain, numbness, and a stinging pain in his hands after sleeping at night.
Main symptoms
Osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebra is most common in:
- Root syndrome;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- Heart syndrome.
Some people suffer from reflex dystrophy syndrome, celiac myelopathy. Diseases in the emotional field, panic attacks of cervical osteochondrosis are often noted.
Rook syndrome
The manifestation of radiation syndrome is caused by the compression (compression) of the spinal nerves of the intervertebral disc, the bone plants of the body, and the vertebrae itself. Due to compression of nerve fibers, local inflammatory reactions occur, accompanied by cold pain in the affected nerves.
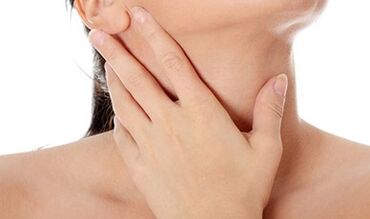
Therefore, with the occurrence of cervical osteochondria disease, symptoms such as pain in the neck, hands, and back areas occur. Unpleasant sensations may be noticed in the heart and stomach. If the pain in the neck is kept, it will increase when turning, and the head is tilted, this condition is called cervical pain. Similarly, pain can have the characteristics of cashew nuts and is called Servicio.
In those areas of nerve-affected nerves, sensitivity is significantly reduced. The muscles in this area become weaker and they may be noticed as their atrophy is reduced with their volume.
Driven arterial syndrome
A vertebral artery is a paired blood vessel that provides 15-30% of the blood supply to the brain. When squeezing the vertebral artery, changes in the intervertebral disc (growth of the vertebrae) notice various chronic manifestations of insufficient oxygen in the central nervous system.
In the development of this state, two stages are distinguished: functional, organic (ischemia). In the first, the main symptoms of vertebral artery syndrome are cervical osteochondral disease. They become more pronounced in head movements while maintaining a position for a long time. Pain is pulsating or pulsating, sensation in the occipital bone, temporal frontal lobe area.
Dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis is also a feature of the functional stage of this syndrome. It has different strengths: from an unstable feeling to a sudden drop or a rapid body spin. Sometimes hearing decreases and a person may be disturbed by noise in his ears. Visual disorders are recorded in front of your eyes as flies.
With the development of pathology, the ischemia stage occurs. It is characterized by temporary cerebral circulation disease in the form of a transient ischemic attack, which usually occurs due to rapid tilt or head rotation.
There are differences in the choices to distinguish vertebral artery syndrome, cervical osteochondrosis, which manifests itself as its own characteristics:
- Descending attack.
- Barre-Lieou syndrome (Posterior cervical syndrome, cervical migraine).
- Migraine.
- Syncopa vertebrae syndrome.
- Ophthalmic syndrome.
- Nutritional dysfunction syndrome.
- Ophthalmic syndrome.
- Kochleo-Investbular syndrome.
- A brief ischemic attack.
With the fallen attack, a person suddenly fell down, leaned back and could not move. No attention was paid to the loss of consciousness, the ability to move independently after a few minutes. This condition is caused by insufficient blood flow to the cerebellum, i. e. the brain stem.
Cervical migraine syndrome is due to the alternating interpretation of peripheral nerve plexus of the vertebral artery or bone plants. This condition is characterized by stupid headaches, which pulsates regularly. For example, if you have to keep the forced position of your head for a long time, they usually occur, for example, when working on a computer, which usually happens after sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow. This trouble with osteocartilage degeneration in the cervical area becomes stronger during the descent, climbing stairs, shaking while transporting, and walking quickly. The pain is located on one aspect of the occipital area and is applied to the anterior part of the head. They can last from minutes to hours.
Syncopa vertebrae syndrome is manifested by insufficient oxygen intake to form the brain reticular formation. This situation is accompanied by short-term fainting, the head stays for a long time, and the neck is in a forced position.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women, in the form of pain, the feeling of sand in the eyes, the spark in front of them, are some manifestations of ophthalmic syndrome. The vision is reduced, the load on the eyes is more obvious, and the vision field is a possible partial loss. Closure occurs and the redness of the conjunctiva is obvious.
The attack of a basic migraine starts with vision in both eyes, noise in the ears, impaired gait, and lubrication of speech. Dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis was also noted in this course variant. Then, a severe headache in the occipital area accompanied by vomiting, and the attack ends with loss of consciousness.
With the development of cochlear syndrome, a person notices a decrease in hearing when the pathological process of the vertebral artery in the ear and the perception of whispering speech is particularly difficult. The feeling of instability of the body in space and the rotation of nearby objects.
Nutritional dysfunction syndrome reflects a disease in the work of the autonomic nervous system in response to squeeze the vertebral artery, surrounding the nerve fibers located around it. It is characterized by high temperature sensing, chills and increased sweating. The feet, palms become cold, wet by touch, and pain is sewn in the heart. Nutritional symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men, and women usually have symptoms of other syndromes.
The fluoroscopic ischemic attack suddenly causes coordination of movement, severe dizziness, speech disorders, nausea and vomiting attacks. These performances are usually reduced if a person is in a horizontal position. After such an attack, the headache, weakness, flies, the flickering in front of the eyes, and the noise in the ears remained for a while.
Sometimes, blood pressure increases and cervical bone-cartilage degeneration is also the result of squeezing the vertebral artery. Therefore, the lack of oxygen is lacking in the brain areas responsible for regulating stress. Under the influence of a sharp increase, it appears in the same nerve impulses as blood pressure drops.
The development stage of osteochondrosis
With the development of degenerative nutritional changes in the intervertebral disc, its developing osteochondrosis goes through multiple stages.
Osteocartilage degeneration in the first degree (preclinical stage) of the cervical area
At this stage, osteochondrosis in the cervical and thoracic cavity is accompanied by muscle tension and discomfort. The cervical spine descends (physiological curves of the spine move forward in the form of a raised) have a slight smoothness. Sometimes pain occurs in this area and the sensitivity of the clavicle area temporarily decreases.
Osteochondrosis 2 degrees
If you have weaknesses in your hands, numbness in the skin on your neck will also reduce the sensitivity of your upper limbs. Vision worsens and noise in the ears is found.
Osteochondrosis 3 degrees
At this stage, there is or is not the rupture of the intervertebral disc formed. The pain on the neck, the neck strap became more obvious, permanent, and was sent into their hands.
Osteochondrosis 4 degrees
The osteocartilage of the cervical vertebra becomes not only the intervertebral discs, vertebrae, but also nerve fibers and blood vessels, which sometimes affect the spinal cord, muscles, muscles, and joints in the body half. The symptoms of the disease are diverse, similar to signs of other pathological conditions. If osteochondrosis manifests, you must consult a doctor immediately for examination.
First aid for severe pain
In severe pain conditions, osteocartilage degeneration treatment should be first designed to prevent osteocartilage degeneration in the cervical spine. To do this, use painkillers medication. They are brought inside to achieve faster results through cervical osteochondrosis, and solutions of these drugs are recommended.
Sometimes pepper is used, and the tool stimulates skin receptors and improves blood circulation in the area of use. Due to this distracting movement, the experienced pain seems less obvious.
physiotherapy
Treatment of cervical bone and cartilage in women, the purpose of physical therapy for men is to:
- Eliminate pain;
- Reduce inflammation;
- spastic muscle relaxation;
- Improve metabolic processes and blood supply to affected areas;
- Release of spinal nerve roots eroded by bone plants (bone growth on vertebrae).
Massage begins with touching the tie from the spine to the upper clavicle, armpit to the area. Then, perform the squeeze because it is the masseur that extends his hand perpendicular to the spine and moves it from top to bottom. In the future, friction is used to heat muscles and improve local blood flow. Starting from the bottom of the skull, the fingers are performed through straight and round motions. Then, in a circular motion, the muscles are kneaded in the area of the collar area. To complete the massage, use vibrational movements in the form of concussion and strokes.